Posted 7:18 a.m. Monday, Feb. 16, 2026
Why it matters for digital accessibility
by Marjorie Bazluki, Senior Instructional Designer in CATL
Overview
The title element is not part of the text of the document but is a property of the whole document. All documents should have title elements that describe their function or purpose. It is not normally displayed in the text of a document itself. The title element should ideally be less than 64 characters in length.
The title element is necessary for users to understand what the page is about, what site they are on, and if the page changed. Meaningful titles can also help with search engine optimization and make content more discoverable.
A Title element in Microsoft Word ( as well as MS Excel and PPT) is a piece of document metadata or a specific style used to identify the document's subject for file management, searching, and is crucial for accessibility and organization. Unlike the visual heading located within the documents body, this property is set via File > Info > Properties, acting as the title for saved files, screen readers, or PDFs.
- Accessibility: Screen readers use this field to identify the file rather than reading the filename, making it essential for document accessibility. If there is no <title> element or if the <title> element is not descriptive and unique, screen readers must read through the entire page to determine its content and purpose.
- Distinct from Style: It differs from the "Title" style, which is just formatting for text within the document body.
Adding a Title Element
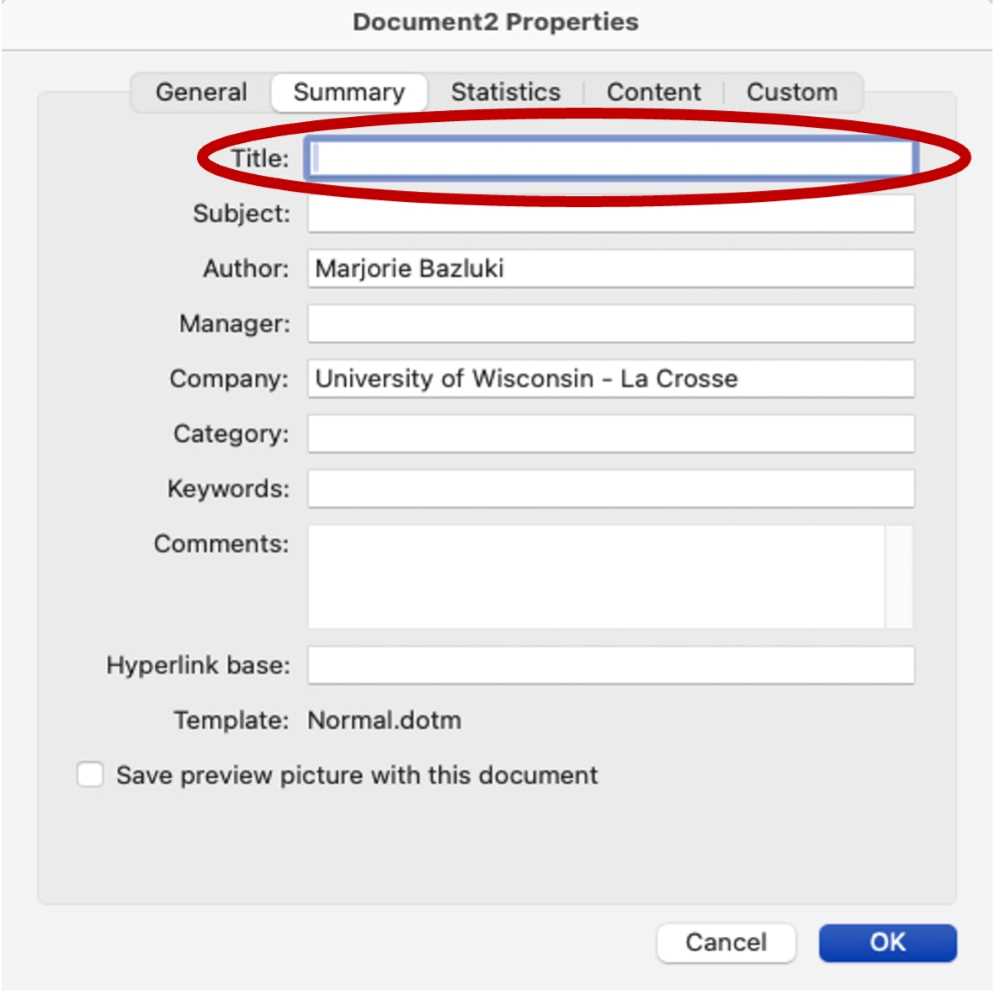
To add a title element in a Microsoft Word or PowerPoint file, select the File menu, then select “Properties…,” this will display the properties window. Selecting the summary tab will reveal the Title field. Enter a title that is meaningful and communicates the overall topic of the document. Select OK to save.
The title element is used in a variety of ways and is helpful for all users. For example:
- The title element is typically the first content announced by screen readers when a new page or document is loaded. A descriptive and unique title helps them quickly understand the page's purpose and navigate the site effectively.
- The title element appears in the title bar of the window for some software applications.
- The title element appears in the tab in web browsers. The text within the <title> element appears in the browser's title bar or the tab for that webpage, helping users navigate between multiple open tabs.
- The title element identifies the page or document when it is added to favorites or bookmarks. When a user bookmarks a page or adds it to their favorites, the browser uses the content of the <title> element as the default title for the saved entry.
- The title element identifies the page in search results as search engines use titles when filtering, ordering, and displaying results.